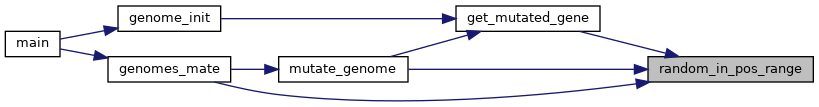
Utility functions for performing different operations on a genome. More...
#include <stdint.h>#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h>
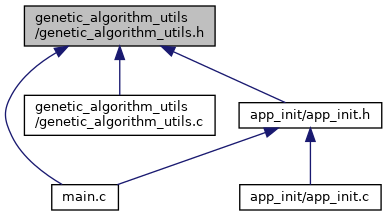
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | genome_t |
| The genome structure. It contains genes, the length of those genes and a fitness score. The genome must be initialized with the genome_target_init function before use. More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | GENE_POOL "!@#$^&*()_-=+,.;:'/\\\"{}[]<>? 1234567890abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" |
| This is a gene pool. You can add your own characters to this as long as they don't mess with the functions and stuff. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef char | gene_t |
| A singular gene is just a character. More... | |
| typedef struct genome_t | genome_t |
| The genome structure. It contains genes, the length of those genes and a fitness score. The genome must be initialized with the genome_target_init function before use. More... | |
Functions | |
| genome_t | genome_target_init (char *string) |
| Initialization of the target genome is slightly different as it already has allocated memory and does not need any mutation. More... | |
| genome_t | genome_init (uint16_t length) |
| Creates a new genome object with allocated memory of the given size. The genome must be manually freed by genome_destroy() after it has been used. More... | |
| void | genome_destroy (genome_t *p_genome) |
| Frees the gene memory allocated to the genome and resets its fitness and length. More... | |
| void | genome_copy (genome_t *destination, const genome_t *source) |
| Performs a deep copy of source to destination while maintaining their original references. More... | |
| void | genome_print (const genome_t genome) |
| Function for printing genomes in a readable format. More... | |
| int | random_in_pos_range (const int upper_limit, const int lower_limit) |
| Provides a pseudo random number between a positive range. More... | |
| char | get_mutated_gene (void) |
| Function for extracting a mutated / random gene from the available gene pool specified in the GENE_POOL macro. More... | |
| int | genome_calculate_fitness (const char *target, const char *genome, uint16_t length) |
| Calculates fitness of the genome based on how close it is to the target. More... | |
| void | genomes_sort_by_fitness (genome_t genomes[], uint16_t genome_count) |
| Sorts the given genome array by ascending fitness. More... | |
| void | mutate_genome (char *genome, uint16_t length, uint16_t max_mutation, uint16_t min_mutation) |
| Provides a mutated genome based on the maximum and minimum possible mutations. More... | |
| void | genomes_mate (const genome_t *p_target, const genome_t *p_parent_1, const genome_t *p_parent_2, genome_t *p_offspring) |
| Mating combines the genomes of two parents over a random crossover point, while the sequence of parents for the crossover is randomly selected. After a crossover, a slight mutation is performed to avoid a local maxima from occurring. Fitness of the new offspring is then calculated, compared to the provided target. More... | |
Detailed Description
Utility functions for performing different operations on a genome.
- Version
- 0.1
- Date
- 21-09-2023
Copyright (c) 2023, Usman Mehmood
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ GENE_POOL
| #define GENE_POOL "!@#$^&*()_-=+,.;:'/\\\"{}[]<>? 1234567890abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" |
This is a gene pool. You can add your own characters to this as long as they don't mess with the functions and stuff.
Typedef Documentation
◆ gene_t
| typedef char gene_t |
A singular gene is just a character.
◆ genome_t
The genome structure. It contains genes, the length of those genes and a fitness score. The genome must be initialized with the genome_target_init function before use.
Function Documentation
◆ genome_calculate_fitness()
| int genome_calculate_fitness | ( | const char * | target, |
| const char * | genome, | ||
| uint16_t | length | ||
| ) |
Calculates fitness of the genome based on how close it is to the target.
- Parameters
-
[in] target target genome string [in] genome input genome string for which fitness has to be calculated [in] length length of both genomes
- Returns
- int fitness score

◆ genome_copy()
Performs a deep copy of source to destination while maintaining their original references.
- Parameters
-
[out] destination [in] source

◆ genome_destroy()
| void genome_destroy | ( | genome_t * | p_genome | ) |
Frees the gene memory allocated to the genome and resets its fitness and length.
- Parameters
-
[out] p_genome pointer to genome

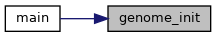
◆ genome_init()
| genome_t genome_init | ( | uint16_t | length | ) |
Creates a new genome object with allocated memory of the given size. The genome must be manually freed by genome_destroy() after it has been used.
- Parameters
-
[in] length length of genome
- Returns
- genome_t a new genome
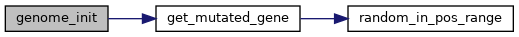
◆ genome_print()
| void genome_print | ( | const genome_t | genome | ) |
Function for printing genomes in a readable format.
- Parameters
-
[in] genome Function for printing genomes in a readable format. [in] genome_1 first genome string [in] genome_2 second genome string
◆ genome_target_init()
| genome_t genome_target_init | ( | char * | string | ) |
Initialization of the target genome is slightly different as it already has allocated memory and does not need any mutation.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] string target string
- Returns
- genome_t initialized target
◆ genomes_mate()
| void genomes_mate | ( | const genome_t * | p_target, |
| const genome_t * | p_parent_1, | ||
| const genome_t * | p_parent_2, | ||
| genome_t * | p_offspring | ||
| ) |
Mating combines the genomes of two parents over a random crossover point, while the sequence of parents for the crossover is randomly selected. After a crossover, a slight mutation is performed to avoid a local maxima from occurring. Fitness of the new offspring is then calculated, compared to the provided target.
- Parameters
-
[in] p_target pointer to target [in] p_parent_1 pointer to parent 1 [in] p_parent_2 pointer to parent 2 [out] p_offspring buffer to store offspring genome in

◆ genomes_sort_by_fitness()
| void genomes_sort_by_fitness | ( | genome_t | genomes[], |
| uint16_t | genome_count | ||
| ) |
Sorts the given genome array by ascending fitness.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] genomes array of genomes [in] genome_count number of genomes in the array

◆ get_mutated_gene()
| char get_mutated_gene | ( | void | ) |
Function for extracting a mutated / random gene from the available gene pool specified in the GENE_POOL macro.
- Returns
- char mutated gene character

◆ mutate_genome()
| void mutate_genome | ( | char * | genome, |
| uint16_t | length, | ||
| uint16_t | max_mutation, | ||
| uint16_t | min_mutation | ||
| ) |
Provides a mutated genome based on the maximum and minimum possible mutations.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] genome genome string to mutate [in] length length of genome [in] max_mutation maximum possible genes to be mutated [in] min_mutation minimum possible genes to be mutated


◆ random_in_pos_range()
| int random_in_pos_range | ( | const int | upper_limit, |
| const int | lower_limit | ||
| ) |
Provides a pseudo random number between a positive range.
- Parameters
-
[in] upper_limit upper limit number [in] lower_limit lower limit number
- Returns
- int pseudo-random number, -ERANGE if upper limit is invalid, -EINVAL if limits are negative